Renewable Energy: A Pathway to Enhanced Resilience
Renewable energy is important for the security of critical infrastructure systems. The grid provides energy to millions of homeowners and business entities who rely on it for everyday functions, yet time and time again it has failed as a reliable source of energy.
Introduction
- Climate change has caused extreme weather changes resulting in widespread and unexpected disasters around the globe. Natural weather events such as hail storms and wildfires are occurring more frequently. This means our reliance on the grid system is more important than ever.
- Renewables can store energy for use at a later date to support these scenarios and provide power when grid systems are unavailable.
- In this post, we will cover why renewable energy should be considered a key element in infrastructure emergency and disaster relief planning.
What is Critical Infrastructure?
Critical infrastructure at its core is the systems, facilities, assets, and technologies that are essential to support the health, safety and economic well-being of a functioning society. For example, hospital buildings and our healthcare system are integral pieces of infrastructure.
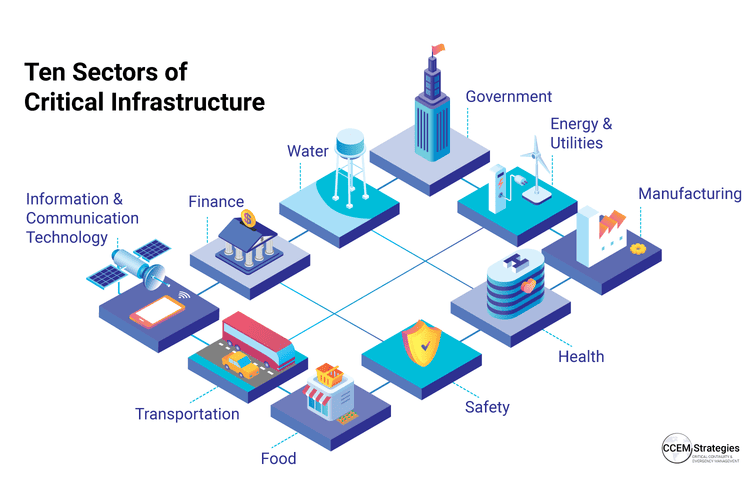
Critical infrastructure is vital in the operation of our modern society, providing essential resources to maintain the functioning of our homes, enterprises, educational institutions, medical facilities, and transportation networks. The absence of this infrastructure would make our standard of living unattainable, and since it is vulnerable to accidents, natural disasters, espionage, and sabotage, it is crucial that we prioritize the safeguarding of these systems.
What is Energy Resiliency?
Energy resiliency has to do with making sure critical infrastructure and the energy supply is durable and dependable in the face of extreme weather and market disruptions. With the rise of extreme weather events and the often unreliable delivery of electricity from the centralized grid, extended power outages are an increasing threat to communities, highlighting the need for energy resilience in critical infrastructure facilities.
Consider the number of extreme weather events – such as wildfires, heat waves, hail storms, and widespread drought – triggering catastrophic power outages. More extreme weather events have been leaving communities without access to power and critical services for extended periods of time.
The severe winter storm that occurred in Texas in 2022 serves as a prime example, where electricity generators were unable to generate sufficient energy in the extreme cold. The power grid failed to meet energy demands, resulting in a state-wide crisis, and numerous fatalities caused by carbon monoxide poisoning, hyperthermia, and the inability to access emergency medical services.
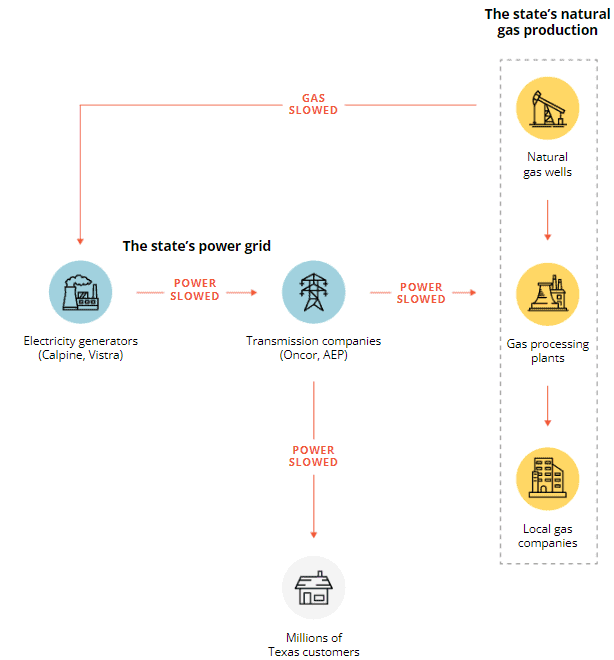
Source: Texas Tribune (2022)
The problem is twofold; the great “Texas Freeze” revealed just how fragile the existing electrical infrastructure has become as more load has been placed on an aging system. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association has estimated the damages caused by the power outages to be in the billions, making it the most expensive catastrophe in Texas’ history.
How you can use Renewable Energy to Optimize your Infrastructure Resilience

There are opportunities for emergency management and sustainability staff to leverage renewable energy assets in support of energy resilience and relief efforts. The cross-functional collaboration between departments to implement sustainable energy resources in emergency management planning will better position communities during times of uncertainty.
Renewable energy can play a critical role in building resilience against climate change and other environmental challenges. Let’s discuss a few examples of how renewable power generation can contribute to creating a resilient infrastructure system and its use cases.
Distributed Energy Systems
Renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines can be installed on rooftops or in communities, allowing for decentralized and resilient energy systems. This means that if there is an interruption to the centralized power grid, these distributed systems can continue to provide power to homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure. One obvious example is when the transmission lines have fallen due to severe hurricanes and many people might lose their access to electricity. Distributed generators as their name suggests are renewables that can be installed locally close to the demand side/site, reducing the risk of disconnection caused by transmission line failure.
Microgrids
Renewable energy sources can be used to create microgrids, which are small, self-contained energy networks that can operate independently of the larger grid. This can be especially important in areas that are prone to power outages due to extreme weather events or other natural disasters. As well as critical infrastructure such as hospitals, municipal transportation, and government buildings.
Energy Storage
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent, which means that they don’t produce power all the time. Energy storage technologies like batteries (lithium/flow), pumped hydro, and new innovative storage methods (compressed air/cryogenic/gravity/thermal) can help store excess energy during times of high production and release it when demand is high. This can help make renewable energy sources more reliable and resilient.
Climate Adaption
Renewable energy can help mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Overall, renewable energy can provide a range of benefits for building resilience, including greater energy security, more reliable power, and reduced vulnerability to climate-related risks. By investing in renewable energy infrastructure and technology, communities can build more resilient energy systems that are better able to withstand environmental challenges.






